Backup and recovery are critical in catastrophic cases that affect an organization’s entire Google Cloud account. Having an untouchable, logically isolated version adds a layer of security for high-risk data.
On September 10, Google Cloud bolstered its backup and disaster recovery services with a non-modifiable vault.
The service is currently in preview mode but will be available to Google Cloud customers in parts of the US, parts of Europe and Taiwan “in the coming months,” the tech giant announced.
The new backup and recovery service is logically isolated
The backup vault feature stands out for being immutable, meaning the data cannot be modified, and indelible, ensuring it cannot be deleted. Data is entered into the backup vault from the backup and disaster recovery service and stored securely to prevent a cyber attack or serious error. Users within the main organization also cannot access the backup vault.
Administrators can set a retention period during which the vault cannot be modified.
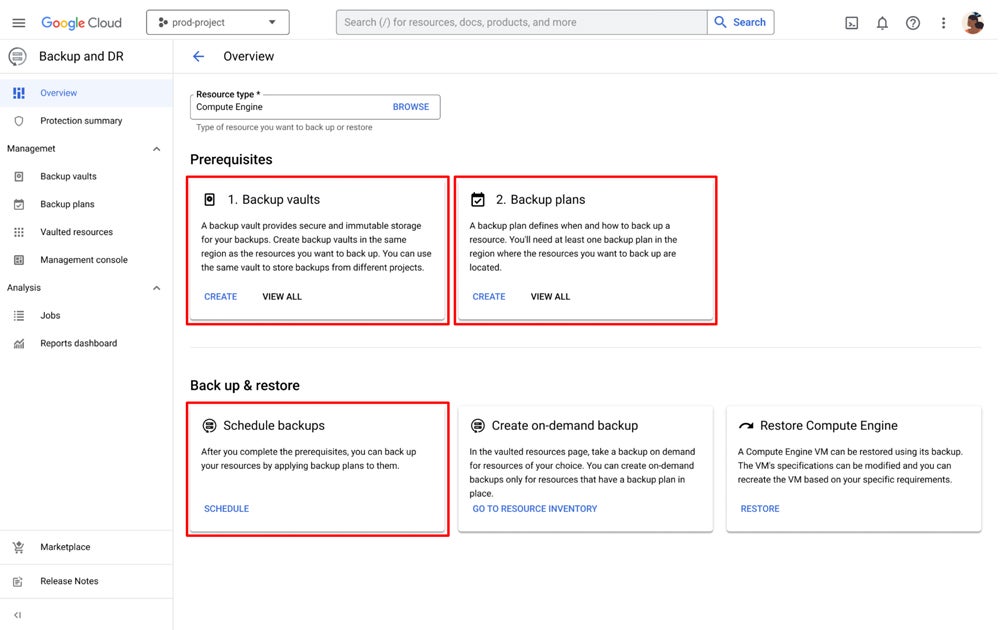
Projects using Google's Compute Engine virtual machine can also store their data in the new warehouse. Warehouses are not connected to the source project and can be based on Compute Engine virtual machines, VMware Engine, Oracle databases, or SQL Server databases.
The backup process for Compute Engine VMs can begin from the moment they are created, integrating into the VM provisioning process. It aligns with Google Cloud identity and access management policies, making setup simpler and more secure, according to Google.
SEE: Microsoft Office 2024 to lose legacy media loader in October as security vulnerabilities hit ActiveX
Create and manage Google Compute Engine virtual machines
Administrators and application developers can manually check scheduled backup and restore jobs, generate reports on failed or skipped jobs, and receive alerts on critical backup-related events. To create a backup using a Compute Engine VM, an administrator simply defines a backup plan within Google Cloud.
Another option, rather than duplicating your Google Cloud backups, is to adopt a multi-cloud system, which has its benefits, as seen with UniSuper's service outage caused by the loss of its Google Cloud account. and backups earlier this year.












