cnn
—
Here's a look at volcanoes, mountains that open into a deposit of molten rock.
More than 80% of the earth's surface, both above and below sea level, is of volcanic origin.
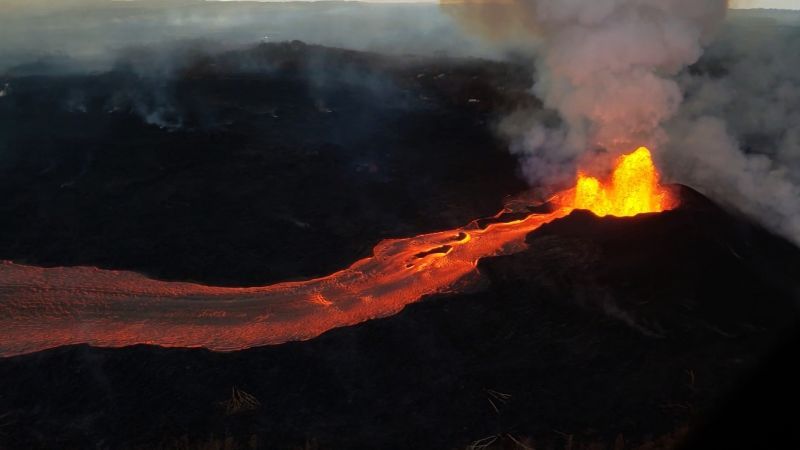
Lava is molten rock from a volcano that reaches the Earth's surface. The liquid rock beneath the Earth's surface is known as magma.
More than 50% of the world's active volcanoes above sea level surround the Pacific Ocean, forming the “Ring of Fire.” The ring extends from New Zealand to the coast of South America.
In 2010, the eruption of a volcano in Iceland disrupted air travel for days across Europe. The eruption expelled a cloud of ash to 30,000 feet in the air. The International Air Transport Authority estimated that the airline industry lost $1.7 billion in revenue due to the disruption.
In 2018, two major eruptions occurred in populated areas. The Kilauea volcano in Hawaii erupted for three months, spewing lava hundreds of meters into the air and destroying about 700 homes. One death was reported. In Guatemala, the Fuego volcano erupted, killing at least 165 people. The two volcanoes erupted in different ways. Slow-moving lava was the destructive force in Hawaii, while the Guatemalan volcano unleashed a deadly mix of ash, rock and volcanic gases.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), there have been more than 650 major volcanic eruptions worldwide between 1800 and 2024.
Volcanoes are generally classified into four main types:
– Cinder cones: These are the simplest type of volcanoes. They are hills, often steep and formed by an accumulation of frozen lava around a vent. When a cinder cone erupts, the ground shakes as the magma rises. Then a powerful explosion spews lava, ash, and gas into the air.
Examples: Paricutin in Mexico, Sunset Crater in Arizona.
– Composite volcanoes or stratovolcanoes: These are symmetrical, cone-shaped and have a system of conduits through which magma flows to the surface. They can rise 8,000 feet above their surroundings.
Examples: Mount St. Helens, Mount Fuji, Mount Shasta, Mount Cotopaxi, Mount Hood, and Mount Rainier.
– Lava domes: These domes are small masses of lava that accumulate around and above the volcano's chimney. Lava domes are commonly found within the craters or on the flanks of large composite volcanoes.
Example: Mont Pelée.
– Shield volcanoes: It is formed when lava cools to form a gently sloping dome. The Hawaiian island chain was created by ocean shield volcanoes.
Examples: Mauna Loa and Kilauea in Hawaii.
Deadliest volcanic eruptions since 1500 AD
The Volcanic Explosivity Index, which measures the relative explosiveness of volcanic eruptions, was devised in 1982. On a scale of 0 to 8, each number represents a tenfold increase in explosive power.
The VEI uses several factors to determine a number, including the volume of material erupted, the height of the eruption plume, and the duration in hours.
Major eruptions: VEI 4 and higher selected (1902-current):
Sources: NOAA Significant Volcanic Eruptions Database and Smithsonian Volcano Database
Note: Dates listed cover the day of maximum explosive activity.
May 6, 1902 – La Soufrière St. Vincent, on the island of Saint Vincent, erupts and causes around 1,680 deaths. (VEI 4)
May 8, 1902 – Pelée in Martinique erupts and kills about 28,000 people. (VEI 4)
October 24, 1902 – Santa María in Guatemala erupts, causing about 2,500 deaths. (VEI 6)
June 6, 1912 – The Novarupta volcano erupts in Alaska, killing two people. It is the largest volcanic eruption of the 20th century. (VEI 6)
January 20, 1913 – Colima in Mexico erupts. The number of deaths is unknown. (VEI 5)
May 19, 1919 – Kelut in Indonesia erupts, causing 5,110 deaths. (VEI 4)
January 21, 1951 – Mount Lamington in Papua New Guinea erupts, killing nearly 3,000 people. (VEI 4)
March 17, 1963 – The Agung in Indonesia explodes and kills more than 1,000 people. (VEI 5)
March 29, 1982 – El Chichón in Mexico erupts, causing 1,879 deaths. (VEI 5)
May 18, 1980 – Mount St. Helens in Washington erupts, killing 57 people. (VEI 5)
June 15, 1991 – Pinatubo in the Philippines erupts and kills about 350 people. (VEI 6)
October 26, 2010 – Merapi in Indonesia erupts, causing 386 deaths. (VEI 4)