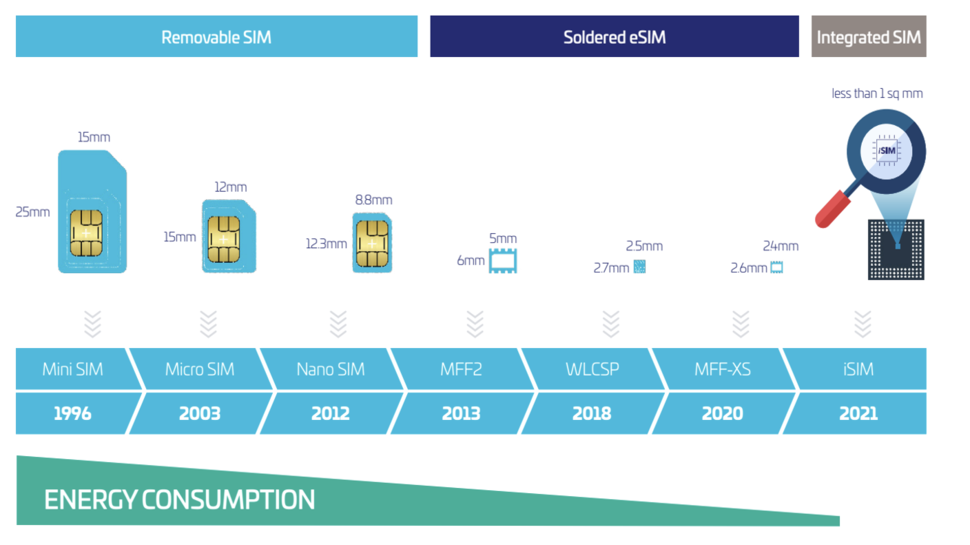
The mobile industry is set to undergo a significant transformation over the next two years, with the imminent shift to embedded SIM cards, or iSIM, new research claims.
A new study from Juniper Research predicts a huge increase in the global number of iSIMs installed in connected devices, rising from 800,000 in 2024 to more than 10 million in 2026.
The release of GSMA's SGP.41/42 specifications, scheduled for late 2025, will drive projected growth of more than 1,200 percent. These guidelines will standardize and streamline the deployment of iSIM-enabled devices.
Expected increase in connections
An iSIM (also known as iUICC – Integrated Universal Integrated Circuit Card) is based on the eSIM (embedded SIM) form factor and is integrated into the device's processor, effectively eliminating the need for a separate SIM module. The integration of iSIM is likely to propel us into an era where the traditional SIM card will be obsolete and networks will preload plans into devices.
The GSMA SGP.41/42 specifications set the framework for In-Factory Profile Provisioning (IFPP) capabilities. IFPP allows the loading of iSIM profiles on a device during production, allowing devices with pre-configured cellular connectivity to be shipped to the desired network.
The Juniper report notes that “Despite increased preparation, it is important to note that as yet there is no industry-wide standard for iSIM technology. Without a standard, manufacturers will not be willing to take the risk of releasing a solution that does not meet an official standard.”
Elisha Sudlow-Poole, author of the Juniper Research report, adds: “eSIM vendors must ensure they provide standards-agnostic platforms that are flexible for upcoming form factors, standards and use case demands. Furthermore, eSIM providers must develop trusted partnerships with manufacturers to ensure adoption of iSIM connectivity services once they are in demand in the market.”
Juniper's study expects the number of iSIM connections to increase to 210 million worldwide by 2028, thanks to adoption opportunities in scenarios such as smart energy meters and remote logistics, where there is a need for small form factor devices and low energy consumption.