The choice between a USB drive and an external hard drive depends entirely on the specific needs and preferences of the user. When choosing, it is important to consider key requirements such as storage capacity, speed, and budget to make the right choice.
While cloud storage and backup facilities are often easy to use and allow instant access to data, there are several reasons why users still prefer an external hard drive. One of them, and not the least, is security. Keeping sensitive data offline means reducing the risk of it being targeted by an online attack. Using cloud backup or cloud storage inevitably involves sharing access with the third party responsible for providing the hosting services. Therefore, if data privacy and portability are paramount, opting for an external hard drive is a sensible choice.
Regional Director for UK and Ireland, Kingston Technology EMEA.
The two key external hard drives
Physical storage comes in a variety of options, but the two main types are fast USB flash drives and solid-state drives (SSDs). A USB flash drive is typically a small device that connects to a device using a dedicated USB port. These handy and ubiquitous devices are easy to carry around, even in a purse or pocket, and are available in a variety of styles and sizes. They are easy to use and are now considered a necessary and inexpensive peripheral for storing files or transferring data between devices without a network connection.
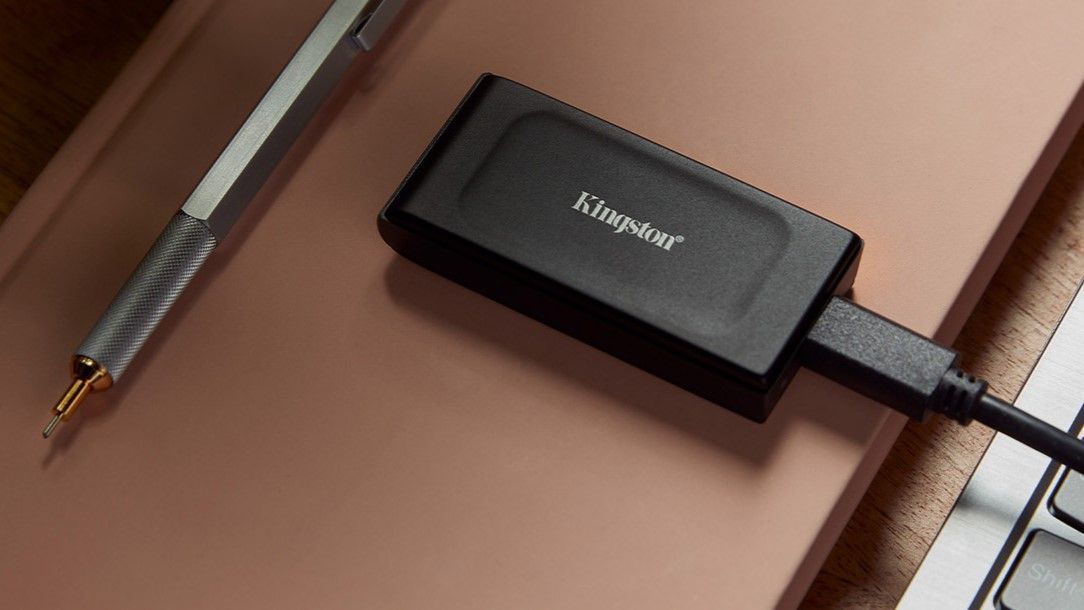
An SSD is a self-contained hard drive with a cable that connects to the user's device, also via the USB port. These drives feature non-volatile flash memory that can facilitate the storage of much larger volumes of data. We offer them in various sizes, from 480 gigabytes (GB) to models that can store up to 4 terabytes (TB) of data.
Analyzing the pros and cons: portability, capacity, performance
The decision between an SSD and a USB flash drive depends entirely on the user’s storage and backup needs. Clearly, due to its compact size, a USB flash drive is the leader in terms of portability. They are so small that they are often used as branded marketing giveaways to hang on a keychain. In comparison, while most external SSDs fit into a small bag and are considered portable, they are slightly heavier than a USB and more suited to quickly reading and writing large volumes of data.
SSD storage capacities are very powerful, making them ideal for larger storage needs. To put this into context, a single computer can have a storage capacity of 500GB, which could hold between approximately 125,000 and 155,000 images. If an external SSD has a capacity of 4 terabytes (eight times the capacity of a standard computer), it could comfortably store millions of documents, images, video content, music files, and many other data.
Although their physical size is small, the capacity of USB flash drives is often larger than users imagine and can be sufficient for the vast majority of storage needs. We have models that allow up to 1 TB of storage, but the standard is 256 GB.
Speed and performance are always important factors to consider when it comes to storage, and SSDs are widely regarded as the fastest external drive option, which also helps to provide efficiency gains for users requiring fast data access. However, the gap between SSDs and USB drives has narrowed with the arrival of USB 3.0 models that have accelerated read and write speeds.
Neither SSDs nor USB flash drives have any moving parts, making them durable. However, SSDs have a longer lifespan and can withstand shocks and vibrations, while USB flash drives are better suited for short-term, less demanding use.
When it comes to price, USB flash drives are typically less expensive than external SSDs, making them the more affordable option. However, if users have demanding storage and backup needs, an external SSD will be the more cost-effective option in the long run. Savings can also be made on different SSD models, depending on usage. SSDs offering up to 1050MB/s read and 1000MB/s write cost around £60 less than those offering up to 2000MB/s read and 2000MB/s write in our range.
Use cases for USB flash drives
For storing and transferring files, documents, photos, and videos, these drives are hard to beat. They have the ability to carry portable applications such as anti-virus tools or productivity software so they can be transferred to different computers, or presentations that can be conveniently and securely delivered at meetings. USB flash drives are frequently used as boot drives and can store system recovery tools to assist with troubleshooting and recovering operating systems, and are used as a physical key to protect access to computers and software. They are simple and affordable, making them ideal for distributing files to colleagues.
External SSD Use Cases
When transferring large files or backing up large volumes of data, SSDs are a faster option. Professional photographers, videographers, graphic designers, and architects can store and edit high-resolution media files and 3D modeling graphics using SSDs, thanks to their fast read and write speeds. Gamers often use SSDs to expand game storage, which helps reduce loading times and improve gaming performance. To help with disaster recovery, SSDs are ideal for full system backups, but can also be used as boot drives for operating systems. Because of their high capacity, SSDs can store and stream large volumes of high-quality media content, including 4K video and high-resolution audio files directly. They are also a popular choice for caching frequently accessed data, which speeds up database performance and server operations.
Summary
Both types of external drives offer secure storage and backup. While USB flash drives offer affordability, flexibility, and convenience in any professional, educational, and personal environment, external SSDs offer solid, high-speed storage for more demanding high-volume data requirements across multiple use cases.
We list the best portable SSDs.
This article was produced as part of TechRadarPro's Expert Insights channel, where we showcase the brightest and brightest minds in the tech industry today. The views expressed here are those of the author, and not necessarily those of TechRadarPro or Future plc. If you're interested in contributing, find out more here: