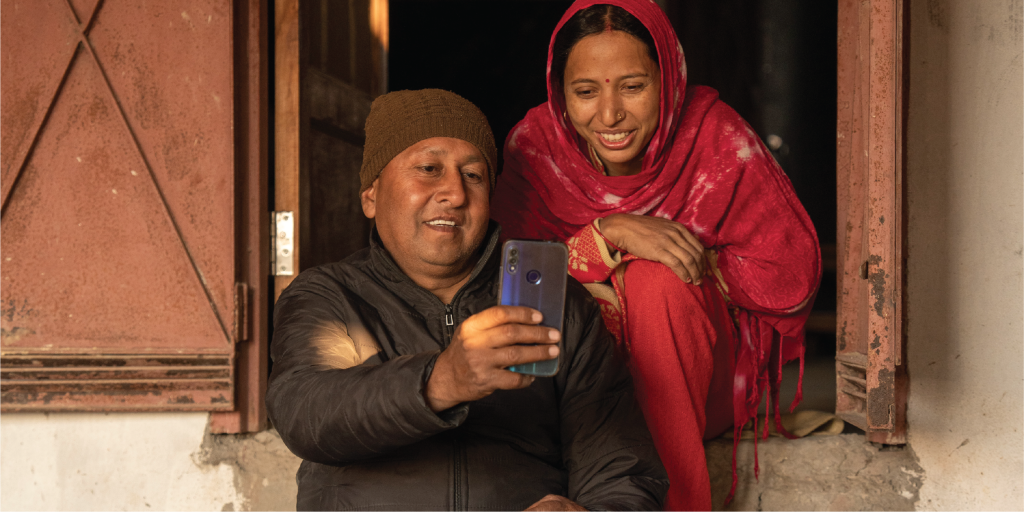
Although 200 million more people began using mobile internet in 2024, much more are needed to help those who live in coverage areas, but they still do not connect to it.
London, September 9, 2025: 4.7 billion people, or 58% of the world population, now use mobile internet services on their own device, according to the annual flagship Mobile Internet connectivity status GSMA report, the global industry agency for the mobile sector.
However, despite 96% of the global population living in areas with mobile internet coverage available for them, 3.1 billion people still do not use it. These people, 38 % of the world's population, sit within what is known as the use gap, with barriers other than the availability of coverage that keeps them offline.
Mobile devices remain the primary, and in many cases, most people access the Internet in low and medium -sized income countries (LMIC), and now represents 84% of global Internet connections.
Progress continues to deliver mobile internet coverage to all, everywhere, with 40 million additional people covered by mobile internet infrastructure last year, the majority (75%) in sub -Saharan Africa. This leaves around 300 million people (4% of the world population) living in what is labeled as the coverage gap, without mobile internet connectivity available.
This means that 3.4 billion people worldwide remained not connected to mobile internet services in 2024, a combination of the use gap and the coverage gap. The overwhelming majority (more than 90%) of these lives in areas with available coverage that remain unable or that are not willing to use. Closing this use gap would provide an estimated $ 3.5 billion in additional GDPs worldwide during the eight years until 2030.
Address imbalances in LMIC
The vast majority (93%) of non -connected lives in LMIC, where they also divide additional challenges. Adults living in rural areas in LMIC have 25% less likely to use mobile internet services than those in urban areas, while women in LMIC have 14% less probabilities than men to be online through mobile devices.
Key barriers to mobile internet adoption include mobile internet awareness, affordability (mainly phones) and digital skills and literacy.
Through the LMIC, the affordability of an entry level device, enabled online, has remained relatively unchanged since 2021 and represents 16% of the average monthly income, increasing 48% for the poorest 20%.
“Although 'The Digital Divide' and 'Connect the Unected' have been on the agenda for more than a decade, the time has come to boost a more significant progress.” Comments Vivek Badrinath, general director of the GSMA. “A $ 30 device could make the phones affordable up to 1.6 billion people who currently have a price coverage with mobile internet coverage available.
“Producing this will require a concerted and collaborative effort between the mobile industry, device manufacturers, political leaders, financial institutions and more, but it is a responsibility that we must all support.”
In 2024, the GSMA launched the Asequinability Coalition of the Manso, an initiative that involves the main global mobile operators, suppliers, players of the device ecosystem, international organizations and financial institutions, such as the World Bank Group, ITI and the Wef Edison alliance, with the aim of accelerating access to smartphones between LMIC populations.
Conduct significant connectivity
Other barriers to use available mobile Internet services include the lack of relevant content, concerns about limited or zero access to fundamental enabling such as consistent electricity.
A key continuous challenge, even among the 4.7 billion people who are already online through mobile devices, is encouraging significant connectivity: users who have a safe, satisfactory, enriching and productive online experience that is affordable in context. While most mobile internet users use it every day, this is often limited to one or two activities, such as verifying a news site or a social media feed.
On the side of coverage, progress continues to be carried out in both standard and more advanced technologies, and 5G services now cover more than half of the world population (54%) and 4G that reach 93%, although the deployment is slowed as the 5G investment is prioritized.
“Getting online has huge and undeniable socio -economic benefits for people and societies.” Badrinath continues. “Essential services such as medical care, education, electronic commerce and banking are now more commonly online, and for billions of people this means mainly on mobile devices.
“In 96% of the world, the infrastructure is in place for people to connect online through mobile devices. Eliminate the remaining barriers to use these services is essential to ensure that existing digital divisions are reduced instead of deepening and many more of these 3,100 million people can benefit from the connectivity that changes life.”
To read the full report and to get more information, see here.
The connectivity report of the Mobile Internet 2025 State is funded by the Office of Foreign Development, Commonwealth and the United Kingdom Development and the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (AIDS) through the GSMA Mobile For Development Foundation, with an investigation funded in part by the GSMA and the Gates Foundation.
Finnish
About the GSMA
GSMA is a global organization that unifies the mobile ecosystem to discover, develop and offer fundamental innovation to positive business environments and social change. Our vision is to unlock all the power of connectivity so that people, industry and society prosper. Representing mobile operators and organizations throughout the mobile ecosystem and adjacent industries, the GSMA offers its members in three broad pillars: connectivity for good, services and solutions of the industry, and scope. This activity includes the progress policy, addressing today's greatest social challenges, underpinning technology and interoperability that make mobile work and providing the world's largest platform to convene the mobile ecosystem in the MWC and M360 events series.
We invite you to get more information at Gsma.com
About Gsma Connected Society
The program of the connected society works with the mobile industry, technology companies, the development community and governments to increase access and adoption of mobile Internet, focusing on population groups disregarded in developing markets.
For more information, visit gsma.com/connectedSociety
Media contacts
GSMA Press Office
[email protected]