Lean project management is a methodology focused on maximizing value and minimizing waste throughout the lifecycle of a project. The lean approach focuses on efficiency. It's about eliminating superfluous elements (whether unnecessary steps, wasted resources, or downtime) and focusing on what adds the most value.
1
Monday.com
Employees by company size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1000-4999), Enterprise (5000+)
Any size of company
Any size of company
Characteristics
Agile development, analytics/reporting, APIs and more
2
Click up
Employees by company size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1000-4999), Enterprise (5000+)
Micro (0-49 employees), Medium (250-999 employees), Corporate (5000+ employees), Large (1000-4999 employees), Small (50-249 employees)
Micro, Medium, Company, Large, Small
Characteristics
Analytics/Reporting, API, Billing and more
3
Wrike
Employees by company size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1000-4999), Enterprise (5000+)
Medium (250-999 employees), Corporate (5000+ employees), Large (1000-4999 employees)
Medium, Business, Large
Characteristics
Agile development, analytics/reporting, APIs and more
What is Lean Project Management?
Lean principles, inspired by the mid-20th century Toyota Production System (TPS), were initially applied to manufacturing but have since spread to other industries, including project management. Lean project management can be thought of as a “less is more” approach to executing projects.
This means fewer resources are used to generate more value by eliminating inefficiencies and continually improving processes. Lean project management seeks to optimize workflows and ensure that each task brings you closer to delivering exactly what your customer needs without additional burdens weighing you down.
5 principles of lean project management
Lean project management revolves around five core principles that guide teams in creating value seamlessly.
Specify value
The first principle leads you to answer: “What am I really delivering to my customer?”
Understanding the real value you’re delivering to customers, whether external or internal, requires a deep dive into what they really care about and what they’d be willing to pay for. For project teams, this means aligning efforts with customer priorities and ensuring that every task directly contributes to the end goal.
For example, in software projects, this might mean focusing on features that solve critical user problems rather than adding unnecessary or ineffective features. Another example would be a sales project that focuses on iterating on a specific aspect of the sign-up process that impacts a target demographic.
Map the value stream
Once you’ve identified the value, it’s time to map out the entire process from start to finish. In lean methodology, this is known as the value stream.
Value stream mapping is not just about listing tasks, but about identifying each step that adds value and eliminating waste wherever possible. A common tool used for this is the kanban board, which is quite popular in agile project management software.
A kanban board visually represents a workflow and helps teams see where bottlenecks or delays may occur. This step fosters transparency in operations and allows teams to refine processes as the project evolves.
For those managing more structured processes, such as waterfall project management, mapping the value stream can help identify areas where delays or inefficiencies commonly occur.
Create flow
Flow is at the core of lean project management. After identifying and eliminating waste, you want to introduce strict sequencing by creating a process where tasks move seamlessly from one stage to the next without unnecessary delays.
Some project teams use a Gantt chart to visualize the flow and better see how project steps relate to each other. This type of tool is particularly useful for projects with a large number of task dependencies.
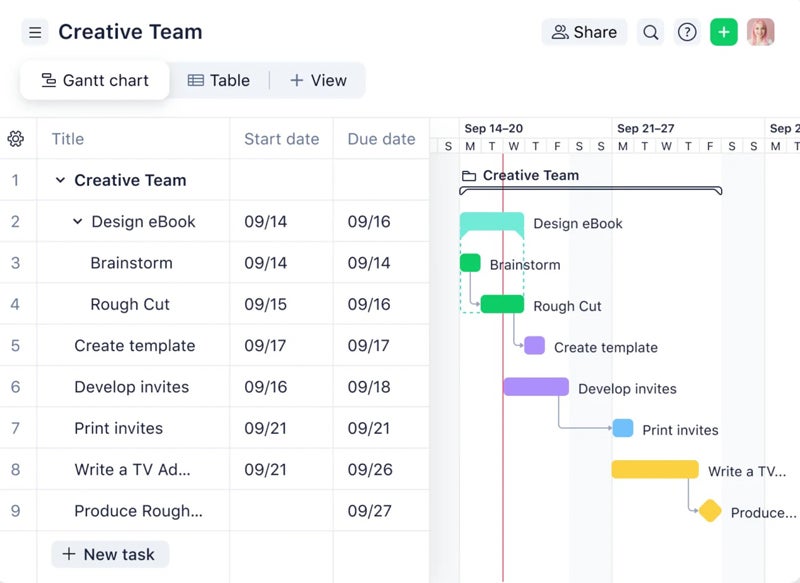
One way to ensure flow is to address bottlenecks. Where does work tend to pile up or slow down? For example, a team might discover that too many approvals or handoffs between departments are causing delays and redo the process to avoid those bottlenecks. Or it might discover that the workload isn’t balanced across team members and adjust that to distribute tasks more evenly.
SEE: Learn more about Gantt charts and how they can be used for lean project management.
Establish attraction
The fourth principle of lean project management is based on the concept of just-in-time production. Instead of pushing work through the production line, lean emphasizes a “pull” system, where tasks are initiated only when there is a demand for them.
This prevents the team from overproducing or wasting resources on features or tasks that might not be needed. In project management, a pull system ensures that resources and time are allocated efficiently, focusing only on what adds value at the moment.
Pursuing perfection
Lean project management is not just about getting things done, but about continually improving the way things are done. As a result, this principle fosters a culture of continuous reflection and improvement.
After successfully completing each project, or even during a project, teams should ask themselves what worked well, what didn’t, and how things can be improved in the future. It’s about striving for perfection through small, incremental changes, often referred to as kaizen, that help teams stay flexible and efficient.
Benefits of lean project management
Greater efficiency and less waste are the main goals of lean methodology, but there are also some additional benefits to consider. Listed below are some of the main benefits of lean project management.
- Greater efficiency: By focusing on eliminating waste and optimizing processes, the lean method helps teams work more efficiently. Tasks are completed faster, bottlenecks are reduced, and unnecessary steps are eliminated, leading to smoother project delivery.
- Cost reduction: The Lean method is designed to identify and eliminate activities that generate waste, which directly reduces costs. Teams avoid overproduction, unnecessary use of resources, and delays that can add financial pressure to projects.
- Greater customer satisfaction: Since the Lean approach focuses on identifying and delivering what the customer truly values, the end result is a product or service that exactly meets their needs. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and can also foster stronger customer relationships.
- Improved adaptability: Lean promotes continuous reflection and improvement, making it easier to adapt to new information, changes in scope, or unexpected challenges. The methodology encourages teams to remain flexible and adjust plans and processes as needed.
- Faster delivery times: Because the Lean approach focuses on creating a smooth flow and eliminating delays, project timelines can be shortened without sacrificing quality. This is especially beneficial in industries where time-to-market is crucial.
Should Your Organization Use Lean Project Management?
If your company often faces resource constraints, tight deadlines, or fluctuating project demands, you should consider lean project management as a structured way to prioritize what matters most and eliminate what doesn't.
Furthermore, Lean’s ability to adapt quickly to change enables organizations to efficiently adapt without adding significant operational costs or delays. By focusing on what adds value to the customer and constantly improving processes, companies can stay agile and competitive in their markets.
For companies in industries such as manufacturing, software development, healthcare or construction, where waste and inefficiency have a huge impact on the bottom line, lean project management would be especially useful.
Whether your goal is cost savings, faster delivery times, or simply a more engaged and efficient workforce, Lean methodology is a proven way to achieve those goals.
For comprehensive project management tools that could improve lean practices, check out this list of the best project management software of 2024.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between lean and agile?
Lean and agile project management share some commonalities, such as their emphasis on flexibility and continuous improvement, but differ in approach and execution.
- Lean primarily aims to eliminate waste and optimize processes to achieve efficiency, while Agile focuses on adaptability and delivering project work increments quickly.
- Agile is more iterative, with short cycles of development, review and adaptation, while Lean is about creating a value-driven, waste-free flow.
- Lean often influences agile practices, but these tend to focus more on frequent delivery and feedback loops.
Is Scrum Lean or Agile?
Scrum is primarily an agile methodology. It focuses on delivering work in short cycles, or sprints, where teams periodically reassess and adapt based on feedback. However, some elements of Scrum align with lean principles, such as minimizing waste and emphasizing continuous improvement. Still, the core framework of Scrum is based on agile values and principles.
Is Kanban Agile or Lean?
Kanban has its roots in lean manufacturing, but is now widely used in agile environments. Kanban focuses on optimizing workflow and reducing bottlenecks, which is a fundamental lean concept. However, it is now often used in agile teams to visualize work and manage flow, making it compatible with both methodologies. So, while Kanban comes from lean thinking, its flexibility makes it useful for agile practices.