Cybercriminals love phishing because it works. It's particularly effective on cloud infrastructure: once they're in, they get access to anything else related to that cloud. According Hornetsecurity Cybersecurity Report 2024, 1.6 billion potentially harmful emails were sent during 2023. Almost half of them used phishing to obtain users' passwords. This makes it by far the most common attack vector. But not all phishing is the same. Phishing campaigns that are highly targeted against specific individuals or types of individuals are known as phishing.
It is important to be able to detect phishing in general. But for phishing targets, it's even more essential to spot the telltale signs, as the damage caused in these attacks tends to be greater.
1
Semperis
Employees by company size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1000-4999), Business (5000+)
Large (between 1,000 and 4,999 employees), enterprise (more than 5,000 employees)
Large, Company
Characteristics
Advanced attack detection, advanced automation, anywhere recovery and more
2
ESET PROTECT Advanced
Employees by company size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1000-4999), Business (5000+)
Any size of company
Any size of company
Characteristics
Advanced Threat Defense, Full Disk Encryption, Modern Endpoint Protection, Server Security
What is phishing?
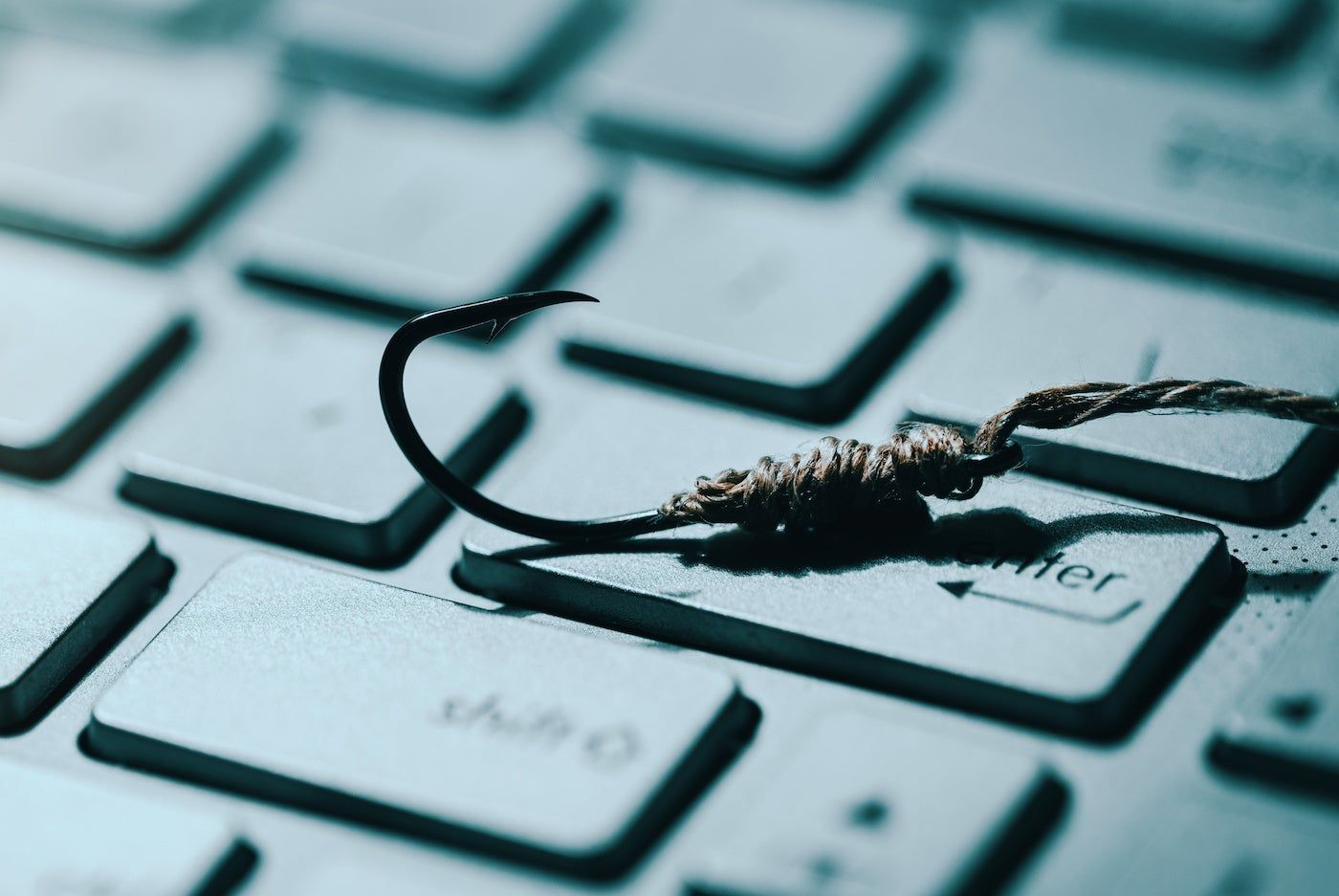
Phishing is basically an online version of fishing, except instead of marine life, the goal is to lure gullible users into revealing passwords and personal information by clicking on a malicious link or opening an attachment. Typical attacks are delivered via email.
Sometimes cybercriminals pose as representatives of cloud service providers and send messages related to a variety of online services and applications.
Phishing messages are often cleverly written. A common tactic is to impersonate well-known brands such as Facebook and Microsoft, as well as banks, Internet service providers, the IRS, and law enforcement agencies. These emails contain the appropriate logos to appear legitimate. Anyone who follows your instructions and hands over their login details or clicks on a link will likely infect your device, download malware, or be locked out of your network and asked to pay a ransom.
Once inside an application running in the cloud, threat actors can expand their attacks to more accounts and services. For example, breaching an organization's Google or Microsoft cloud gives the attacker access to email accounts, contact lists, and document creation. By targeting a phishing campaign to obtain cloud credentials, criminals have a better chance of attracting a larger payload.
What is phishing?
While phishing is widespread in the sense that a phishing email can be sent to millions of people, spear phishing is highly targeted. The goal is to compromise the credentials of a specific person, such as the CEO or CFO of a company, as we reported in 2023.
In Spear phishing, messages are carefully crafted. Criminals study social media posts and profiles to obtain as much data as possible about a victim. They can even gain access to the person's email and remain invisible for months while they evaluate the type of traffic the person receives. Phishing messages are designed to be much more credible than generic phishing attempts because they are based on data taken from the person's life and work. Recognition makes the phishing email, text, or call highly personalized.
In the cloud, a high-value target could be a person with administrative privileges for systems spanning thousands of individual accounts. By compromising that identity, hackers have free rein to infect thousands more users.
Spear phishing vs. phishing: Identify the differences
Many of the red flags for potential phishing emails also apply to phishing. They include typos in text, poor grammar, emails from unknown recipients, suspicious links, a false sense of urgency, or email requests to enter sensitive information. What distinguishes Spear phishing from regular phishing is that the message usually has much more detail and takes on a familiar tone. The level of surprise and urgency is usually increased in phishing and often involves the transfer of money.
Phishing example
Phishing emails reach a large number of people and not specific individuals. For example, you could send an email to thousands of people or everyone in a company telling them that IT wants them to verify their credentials by clicking on a link and entering them into a form.
Phishing example
Spear phishing is more specific. For example, a CEO's assistant could be the target of a criminal posing as an email from the CEO. The hacker has been monitoring emails and social media messages for months and knows that a big deal is about to happen at a point where the CEO is overseas, sealing the deal. The criminal then sends an email that appears to be from the CEO or even sent from the CEO's account, telling the assistant that there has been a change of plans and to immediately transfer $x million to a new account.
Protect your organization from phishing and phishing attacks
There are several measures organizations can take to protect themselves from phishing and phishing attacks.
Install an antispam filter
A spam filter will detect up to 99% of spam and phishing emails. They are not infallible. But they capture a lot. Spam filters are continually updated based on the latest scams and hacker tricks, so don't be left without one.
Use a VPN
A VPN is a virtual private network that provides those working remotely with a greater degree of message privacy than when using the Internet. The user connects through an encrypted tunnel, making it difficult for anyone else to intercept the data. Using a VPN also makes it harder for phishers to succeed by adding extra layers of protection to email messages and cloud usage.
Take advantage of multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions
AMF should always be implemented. If someone compromises a password, they cannot cause any harm as they must be authenticated courtesy of an authenticator app, a code sent via text message, a biometric method, or some other authentication method.
Install antivirus software
Antivirus software was the original security safeguard that promised to prevent systems from becoming infected with viruses. For a while they did the job. But hackers discovered ways to get around them. However, without it, a large amount of malware would wreak havoc on the company. Make sure antivirus software is part of your security arsenal, as it detects all types of viruses and malware.
Deploy cloud security posture management software
Cloud security posture management continually monitors cloud risk through a combination of prevention, detection, response, and prediction steps that address areas where risk may next appear. This technology adds a predictive approach, which can make a big difference in reducing phishing and phishing scams.












