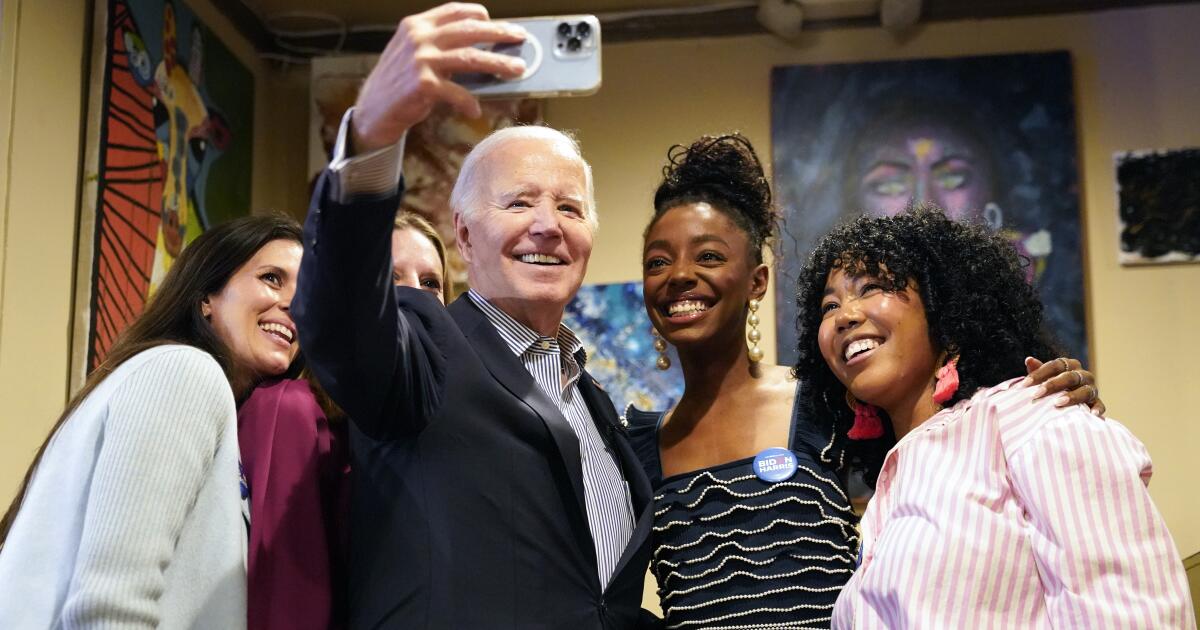
For a long time, landlines were the best option available to most businesses. They were easy to install and use, did not require special equipment or technical knowledge, and even the costs of long-distance calls seemed reasonable.
But in recent years, VoIP technology has evolved to offer the same or better reliability than landlines, often at a lower cost, and to include features like video conferencing and messaging. Plus, phone carriers are no longer forced to maintain traditional PSTN landlines, instead replacing old copper with fiber.
When to Consider VoIP vs. Landline
VoIP is likely to be the default choice in the future, but can landlines still be around? There are some specific situations where you might want to use landlines alone or with a hybrid VoIP setup.
Scenario 1: You have a lot of analog equipment
If you've invested a lot of time and money into building a PBX infrastructure, the costs of changing all the phones, switchboards, wiring, and calling plans may make you think twice about upgrading.
Imagine running a hotel with a complex switchboard, hundreds of phones and cables running to every room. Going straight to VoIP would be expensive and could annoy guests to the point of affecting bookings.
At the same time, your analog equipment will one day need to be replaced. The good news is that you can make the transition to VoIP without a sudden upgrade.
Hardware such as analog telephone adapters and SIP trunking technology can connect your old phones to VoIP without having to replace the equipment. It is even possible to use both technologies as a hybrid solution.
Scenario 2: You don't have broadband access in your area
If you run a small business in a very remote area, it's not uncommon for “high-speed Internet” to crawl like a turtle. In some rural areas, the only option for connecting to the Internet is still a landline modem with dial-up access.
As of mid-2023, about 42 million Americans did not have access to broadband internet. They still rely on old landlines, mobile data, or at best, satellite internet. However, each of these connection types has drawbacks that make them not an ideal choice for VoIP.
VoIP doesn't require a lot of bandwidth, but it does require a broadband connection with a minimum speed of 25Mbps or higher to work. VoIP thrives on a fast, reliable Internet connection; the requirements only increase with more lines.
If your region lacks broadband access, here are some options that might make VoIP possible:
- Star Link: Starlink offers faster internet than most other satellite providers, with plans ranging from 40 to 220 Mbps with minimal latency. You can access Starlink services from almost anywhere.
- Fixed Wireless Access: Some internet providers are extending their reach by using 4G and 5G towers or other fixed points to transmit data wirelessly. Plans and prices vary, but most carriers claim speeds between 100 and 300 Mbps, depending on proximity to a hotspot.
- Community wireless networks: In some rural communities, residents collaborate to build and operate their own wireless networks. This can be a cost-effective option, but requires community involvement and technical expertise to install and maintain.
Scenario 3: You have a large or geographically dispersed team
For businesses with teams spread across countries or continents, keeping costs down is critical. Most landline providers help limit costs by offering lower international calling rates or fixed monthly rates for calls to specific countries.
However, many of today's VoIP providers include international calling along with other features. VoIP can help streamline operations and reduce costs if your business has multiple geographic locations.
Cloud-based VoIP can serve your entire team, regardless of location, with little physical infrastructure. Remote workers can communicate just as efficiently as employees in the office. Some providers even offer dedicated international numbers, allowing local calls to be made in different regions.
You can also consider a hybrid approach where you retain landlines for specific high-volume international calls, which offer a cost advantage, while using VoIP for general communication and collaboration within and between teams.
Scenario 4: You have unique security concerns
It is a common fear that Internet-based communications are not secure enough for data storage, leading some companies to use landlines and store files only on local servers.
The problem is that work can't be done in a vacuum. These companies end up using a patchwork system of communication: phones for this, email for that, and yet another chat program for support. Ironically, this haphazard approach can put systems at greater risk, as each program opens new doors to security threats.
Businesses with a robust IT infrastructure can effectively manage network security, but smaller businesses can benefit from the outsourced security offered by cloud-based VoIP platforms.
Most vendors offer security features such as encryption protocols (AES-256), access controls, and compliance certifications to ensure your data is protected from hackers, spies, and other threats. Additionally, vendors regularly audit their systems to ensure ongoing protection and employ intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats before they wreak havoc.
In other words, they take care of the highly technical aspects and have dedicated teams to help them. In turn, businesses can create an even more secure environment with standard security practices, such as using strong passwords, protecting firmware on VoIP phones, and implementing firewalls.
Scenario 5: You have concerns about data privacy and regulatory compliance
If your organization is concerned about maintaining strict data privacy standards and meeting compliance regulations when using VoIP, you can do so with the right configuration and by following a few guidelines.
Some of the major VoIP providers, such as Nextiva, offer HIPAA-compliant plans. However, it's important to note that some features, such as text messaging and voicemail transcription, are not compliant. Another example is that most businesses must comply with GDPR guidelines, including data access rights and deletion procedures.
Providers like Nextiva know the regulations and can help you learn how to comply within the limitations.
Security and compliance are essential for any business, but we've reached a point where it's difficult to do business without the convenience that VoIP offers.
VoIP communication vs. landline communication
While there are some scenarios where you might consider keeping your landline or incorporating VoIP into your existing system, there are technical differences in how these systems work.
How landlines work
Landlines send analog voice signals over copper wires. These signals don't require an internet connection and offer consistent quality, but they travel at slower speeds and the wires are susceptible to physical damage.
Because the infrastructure is relatively simple, the investment is minimal: you may only need phones and a modem if you still use dial-up Internet. But you'll need a more complex setup if you have a phone system with multiple lines or use your landline for calling along with a dedicated Internet connection.
How VoIP Works
VoIP works differently because it operates digitally. An analog-to-digital converter converts voice into digital data packets. This data is compressed using audio codecs such as G.711 or G.722, routed through servers, and sent over the Internet using protocols such as IP (Internet Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) to speed up transmission.
At the receiving end, the packets are reassembled and converted back into analog signals, allowing you to hear the original voice. VoIP communication is much faster, smoother, and clearer, as long as you have a reliable, high-speed Internet connection.