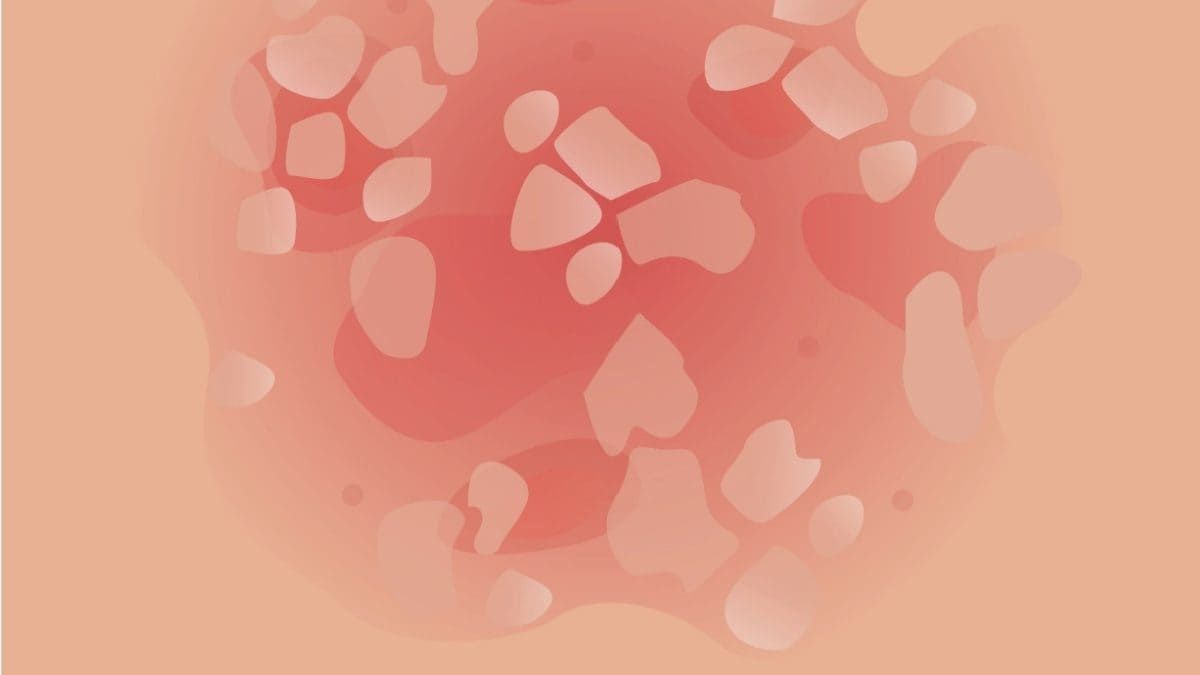
Psoriasis presents a multifaceted challenge in India, with significant differences in prevalence and impact based on gender.
Psoriasis affects between 0.44% and 2.8% of the Indian population, mainly adults, and men are twice as likely to be affected.
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, is a major health problem affecting a considerable portion of the Indian population. It is estimated that between 0.44% and 2.8% of the Indian population suffers from this disease, with a clear predominance in adults. A striking feature of this prevalence is the notable gender disparity: men are reported to be twice as likely to develop psoriasis compared to women.
Dr Rashmi Aderao, consultant dermatologist at Ruby Hall Clinic in Pune, looks at the factors behind this disparity and examines the broader impact of psoriasis on those affected.
In India, the prevalence of psoriasis varies widely, reflecting regional differences and variable access to healthcare. Most cases occur in adults, usually between the ages of 15 and 35 years. However, psoriasis is not limited to these age groups and can occur at any stage of life, indicating that the disease poses a problem for a broad demographic.
The marked difference in psoriasis rates between men and women calls for a closer look at several potentially influential factors.
- Hormonal dynamicsHormonal changes can significantly affect the risk of psoriasis. Estrogen, which is more common in women, is known for its anti-inflammatory effects, which may offer a protective advantage against autoimmune disorders such as psoriasis. In contrast, testosterone, which is more common in men, may enhance inflammatory processes, thus increasing susceptibility to psoriasis.
- Genetic factorsGenetics likely play a crucial role in susceptibility to psoriasis. Although research is ongoing, evidence suggests that men may inherit specific genetic markers that elevate their risk. Certain genes involved in immune regulation and skin cell turnover may be more prevalent in men, contributing to a higher incidence of psoriasis.
- Environmental and occupational factorsMen, especially in the Indian context, are often exposed to environmental and occupational factors that can trigger psoriasis, such as stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, and exposure to harsh chemicals or prolonged sun exposure. These factors not only contribute to the onset of psoriasis but can also exacerbate existing symptoms.
- Variations of the immune systemMen and women exhibit different immune system responses. Men's immune systems are often more prone to intense inflammatory reactions, which can lead to a higher incidence of autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis. This heightened inflammatory response could be a key reason for the increased prevalence among men. The higher incidence of psoriasis in men carries important implications for their overall well-being. Men are more likely to suffer from severe forms of the disease, which can lead to greater physical discomfort and a higher likelihood of developing complications such as psoriatic arthritis. In addition, societal expectations often pressure men to be the primary breadwinner, leading them to postpone or avoid treatment. This can exacerbate their disease and contribute to a cycle of worsening health problems.
The psychological impact of psoriasis on men can be profound. The visible nature of the disease, combined with social stigma, often results in feelings of shame, social isolation, and depression. These mental health issues are frequently intensified by the chronic nature of psoriasis and its physical effects, making it critical for affected men to seek comprehensive care and support. Psoriasis presents a multifaceted challenge in India, with significant differences in prevalence and impact between genders. Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to these disparities is essential to improving treatment and support for those affected. As research continues to unravel the complexities of psoriasis, it is vital to address both the physical and psychological needs of people living with this condition, with a particular focus on the unique challenges faced by men.